Protozoan parasites in humans are the causative agents of protozoan infection (or protozoosis). The disease is contagious, threatening complications and serious consequences. Therefore, protozoosis requires timely diagnosis, accurate identification of pathogens and proper treatment.
Are protozoan parasites
This is a group of single -celled microorganisms that are unable to generate nutrients independently. In the process of life, they use other beings, causing them serious illness. The most common human protozoan parasites are listed below:
- flagella - giardia, leishmania, trichomonas, trypanosoma;
- sarcodal - amoebic dysentery;
- ciliates - bursaria, balantidia;
- sporozoa - plasmodium malaria, coccidia, piroplasma.
Trypanosoma
The simplest parasite whose life cycle occurs in the bodies of ungulates (antelopes) or infected people. The carrier is a tse-tse fly, which, when bitten by a person, injects saliva with protozoa into its skin.
On a note!
For disease progression (African trypanosomiasis or sleep disease), the identification of approximately 400 trypanosomes is necessary. With one bite of a tse-tse fly, up to half a million individuals of the parasite fall.
Characteristics of parasitism and disease:
- trypanosomes initially circulate in the bloodstream of infected people, causing trypanids on the skin (swelling of the face, eyelids), fever with temperatures up to 40 ° C, swollen lymph nodes;
- then unicellular parasites migrate into the cerebrospinal fluid, causing drowsiness, iridocyclitis, chronic fatigue, lethargy, impaired speech, coordination;
- advanced forms of trypanosomiasis are marked by spasms in the limbs, epileptic seizures, nervous and physical fatigue, respiratory paralysis, coma, and death.
For the diagnosis of trypanosomiasis, Romanovsky-Giemsa test, immunofluorescence reaction, enzyme immunoassay (ELISA), lymph node puncture were used. Confirmation of the diagnosis is often done by inserting the sick person’s blood into a laboratory pig. Treatment of sleep disorders involves the intake of special medications. In the absence of therapy with a high degree of probability, patient death is possible.
lamblia
Microscopic protozoa (synonyms - giardia or giardia) with four pairs of flagella are full -cycle parasites in the human body. Under certain circumstances, they cause giardiasis. Giardia is attached to the wall of the small intestine by large inhalers, often settling in the liver ducts, gallbladder and other internal organs.
On a note!
Infection with protozoa occurs with food, water, in unclean conditions. Giardia cysts with embryos remain invasive in the environment for a long time (up to 3 months in fresh water, up to 4 months in sewage). Diagnosis of protozoa is carried out by microscopy of cysts and adults in feces, blood, detection of antibodies in ELISA studies.
Leishmania
These flagged protozoa cause leishmaniasis, which is common in tropical and subtropical countries. Infection occurs in a contagious way - when bitten with the saliva of blood -sucking insects, animals (dogs, ground squirrels). Mosquitoes, gnats, gadflies, fleas can be carriers. There are two types of leishmaniasis in humans:
- skin and mucocutaneous forms (pendinskaya ulcers) - leishmania live and multiply in human skin, causing inflammation, swelling, ulcers, trophic ulcers, damage to the respiratory tract;
- visceral form - leishmania resides in internal organs (spleen, liver, lungs, heart).
A hallmark of skin leishmaniasis is the formation of brownish nodules (leishmaniomas) at the site of insect bites. Then they are replaced by round ulcers, difficult to heal with purulent exudates. The disease lasts for 1-2 years, leaving scars on the skin. In its visceral form, leishmaniasis causes dysfunction of the adrenal glands, kidneys, liver, and spleen. When diagnosing leishmania, it is found in the bone marrow, lymph nodes, skin abrasions, and blood.
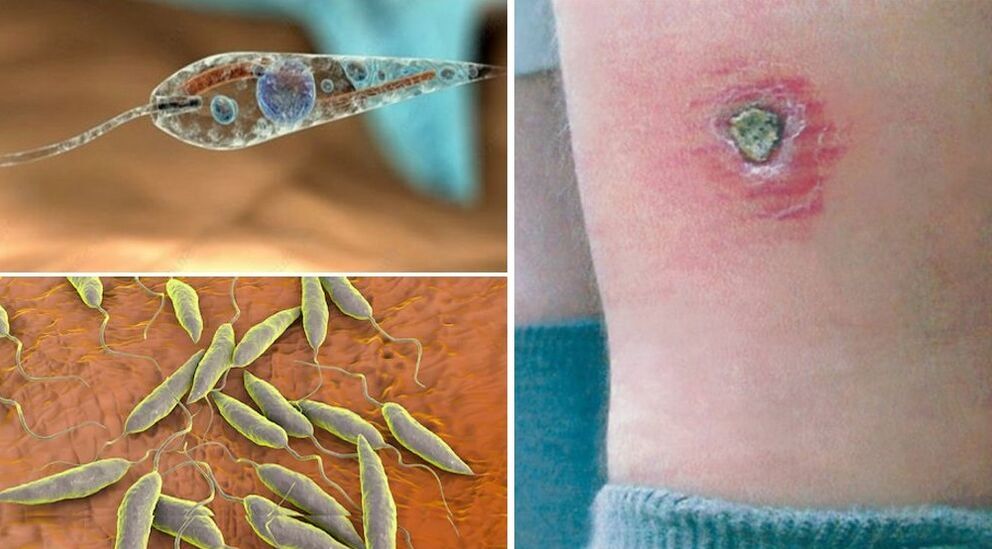
On a note!
Treatment of leishmaniasis involves quarantine measures, isolation of patients and medications.
Trichomonas
These are the simplest parasites in the human internal environment, transmitted sexually, through household contact or as a result of birth infection from mother to child. There are oral, intestinal and urogenital types of Trichomonas. Protozoa are the causative agents of trichomoniasis/trichomoniasis. Urogenital trichomoniasis of the genitourinary system is widespread. The chronic form of the disease threatens with impotence and persistent infertility. Characteristics of Trichomonas parasitism:
- body size - up to 18 microns, fast moving due to mobile flagella;
- resistant to drugs, determines the course of chronic trichomoniasis;
- quickly dies in the environment, in the air, in direct sunlight;
- long stays on wet wipes, sponges, towels, soap dishes;
- frequent infections during vaginal, oral-vaginal sexual intercourse;
- Trichomonas contributes to the development of candidiasis, vulvitis, chlamydia, gonorrhea, cystitis.
The diagnosis of trichomoniasis includes the detection of Trichomonas in a swab of the genitals. Treatment involves the use of medications, treatment with antiseptics. Therapy is performed on both partners to prevent relapse. Prevention of urogenital trichomoniasis includes measures recommended for all venereal diseases.
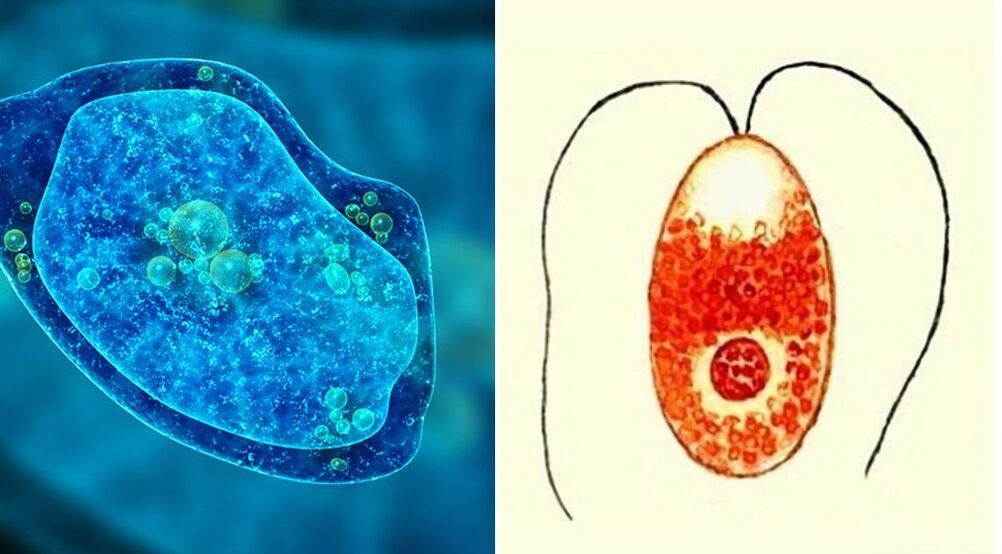
amoebic dysentery
These sarcode microorganisms are parasites that cause dangerous diseases to humans. There are two forms of dysentery amoebiasis - intestinal and extraintestinal (hepatic or pulmonary). The disease begins 7-10 days after infection with symptoms-bloody diarrhea, fever, vomiting.
If left untreated, the consequences of amoebiasis develop - dehydration, fatigue, weakness, internal bleeding, liver abscess. Infection most often occurs through the oral-fecal route. Carriers of amoeba cysts can be insects - flies, gadflies. During diagnosis, a tissue form of protozoa is found in the feces. Treatment of amoebiasis is stationary, with the use of antibiotics.
Plasmodium malaria
The simplest representative of sporozoan, the causative agent of a dangerous disease - malaria. The human body serves as an incubator where the life cycle of parasites takes place. Characteristics of parasitism:
- infection with plasmodium sporozoites occurs when bitten by malaria mosquitoes;
- sporozoites enter the bloodstream with the saliva of infected insects;
- sporozoites settle in the liver, penetrating into the cells (hepatocytes);
- here merozoites are formed by replication of mitosis;
- when hepatocytes are destroyed, merozoites penetrate into erythrocytes;
- from merozoites as a result of the sexual cycle, gametocytes are formed;
- mosquitoes become infected with gametocytes when bitten by an infected person;
- in the body of a mosquito, gametocytes enter the oocyst and then into the sporozoite;
- mosquitoes infect healthy people, and the cycle repeats.
The destruction of erythrocytes and the release of gametocytes into the bloodstream are accompanied in humans by attacks of fever, vomiting, anemia, seizures, and joint pain. In severe cases, the risk of death increases. Malaria often takes on a recurrent character with a phase of deterioration and rest. Different protozoa cause tropical malaria, three days and four days. The main therapeutic and diagnostic agents are quinine - natural from cinchona or artificially synthesized.
Infusoria balantidia coli
The causative agent of balantidia (or infusory dysentery) lives in the large intestine, causing bleeding ulcers on its walls. Infection with protozoa occurs from domestic animals, especially the carrier is pigs. Anatomical features and parasitism:
- balantidia body oval -shaped with a dense and strong shell (pelican);
- on the surface there are many cilia which function for movement;
- sexual forms of the parasite are required for reproduction by easy cleavage;
- asexual forms (cysts) enter the environment with feces;
- The route of human infection with cysts is oral-fecal.
Relocation of protozoa in the intestine is accompanied in humans with headache, vomiting, and dyspepsia. The acute stage of balantidiasis is indicated by a state of fever, signs of severe intoxication, loose stools with blood clots. In the absence of timely treatment, fatal outcomes are possible.
Toxoplasma gondii
Microscopic crescent -shaped spore protozoa of the order Coccidia are widely distributed in the environment. They are the causative agent of the disease - toxoplasmosis. In healthy people, ingested pests are destroyed by immune cells. Characteristics of diseases caused by protozoan parasites in humans:
- often toxoplasmosis is asymptomatic, after recovery, immunity is developed;
- parasites affect the organs of vision, reproductive system, nerves, lymph, liver, spleen;
- during pregnancy, toxoplasmosis causes severe congenital pathology of the fetus or its death;
- acute form proceeds with seizures, paralysis, liver hypertrophy, heart problems;
- in the course of chronic, cardiac dysfunction, damage to the organs of vision is possible.
The main host of protozoa is cats. In their bodies, large colonies of Toxoplasma form from oocysts. People are intermediate hosts, they are infected through food, domestic contact or mouth-feces.






































